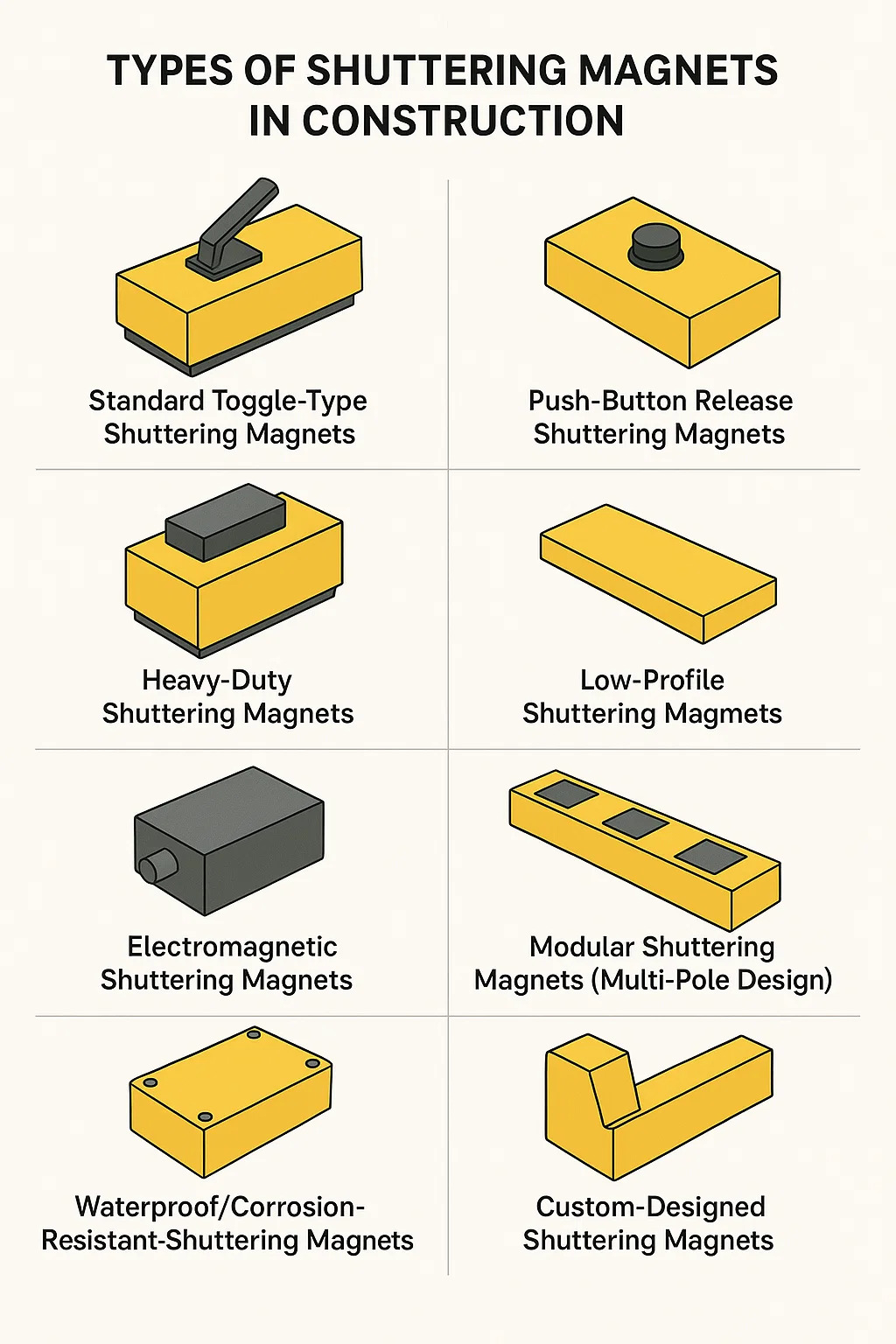
Types of Shuttering Magnets in Construction
Shuttering magnets are categorized based on their design, application, and magnetic activation method. Below are the main types used in formwork systems:
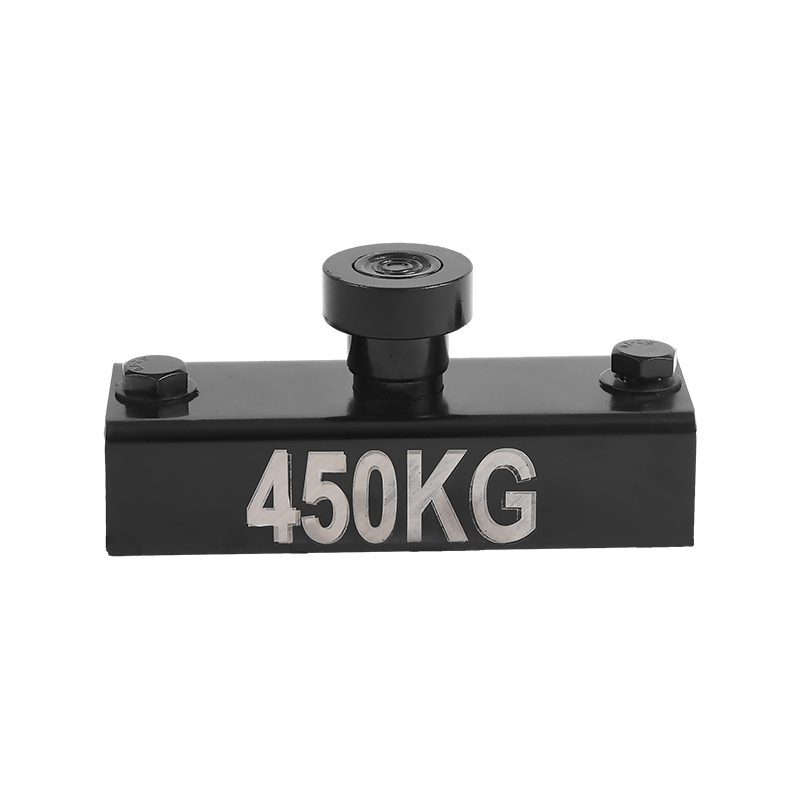
1. Standard Toggle-Type Shuttering Magnets
Design: Equipped with a manual lever or toggle switch to engage/disengage the magnetic force.
Function: Used for general formwork applications where steel-backed panels need quick clamping.
Common Uses:
Holding vertical wall forms in place.
Securing column formwork during concrete pouring.
Advantages:
Simple operation (flip the lever to activate).
Durable and reusable.
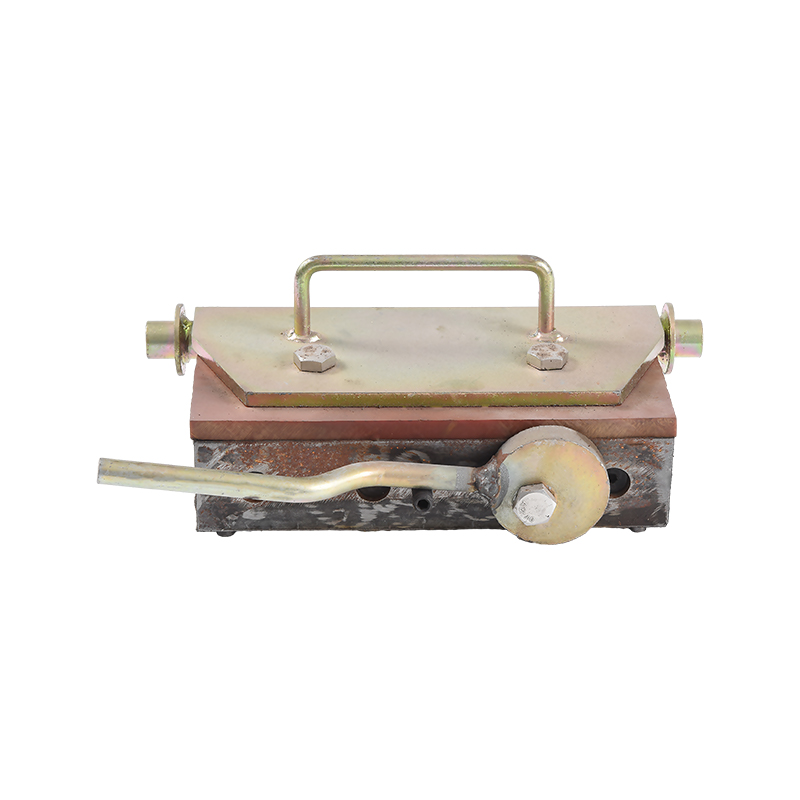
2. Push-Button Release Shuttering Magnets
Design: Features a push-button mechanism for instant magnetic engagement.
Function: Faster to operate than toggle-type magnets, allowing one-handed use.
Common Uses:
High-speed formwork assembly.
Situations requiring frequent adjustments.
Advantages:
Quick activation/deactivation.
Reduced worker fatigue.
3. Heavy-Duty Shuttering Magnets
Design: Built with reinforced steel casing and stronger magnetic cores.
Function: Used for large or heavily loaded formwork systems.
Common Uses:
Securing thick concrete walls or deep foundations.
Supporting heavy-duty steel forms in bridge construction.
Advantages:
Higher holding power for demanding applications.
Resistant to deformation under stress.
4. Low-Profile Shuttering Magnets
Design: Compact and slim for tight spaces.
Function: Used where standard magnets are too bulky.
Common Uses:
Narrow column forms.
Thin-wall concrete structures.
Advantages:
Fits in confined areas.
Lightweight yet strong.
5. Electromagnetic Shuttering Magnets
Design: Uses electrical current to generate a magnetic field (instead of permanent magnets).
Function: Provides adjustable magnetic strength and remote control capability.
Common Uses:
Automated or robotic formwork systems.
High-precision concrete molding.
Advantages:
Magnetic force can be fine-tuned.
Can be turned off completely without residual magnetism.
6. Modular Shuttering Magnets (Multi-Pole Design)
Design: Contains multiple magnetic zones for better load distribution.
Function: Prevents formwork distortion by evenly spreading clamping force.
Common Uses:
Large-panel formwork systems.
Curved or irregular concrete structures.
Advantages:
Reduces risk of formwork bulging.
More stable than single-point magnets.
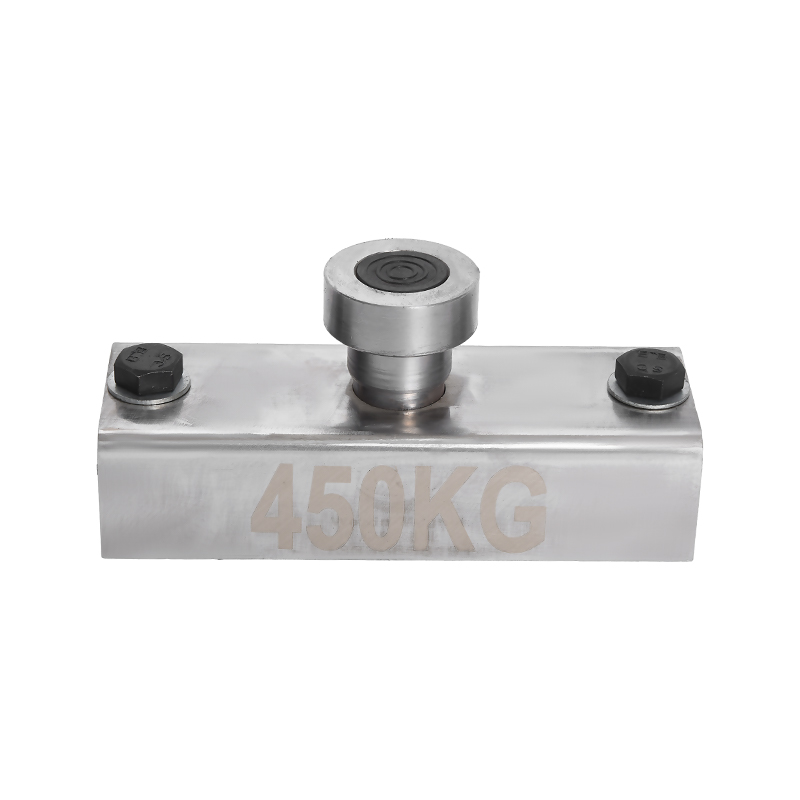
7. Waterproof/Corrosion-Resistant Shuttering Magnets
Design: Sealed housing to prevent moisture or concrete ingress.
Function: Used in wet or corrosive environments.
Common Uses:
Marine construction (piers, seawalls).
Underground or water-retaining structures.
Advantages:
Longer lifespan in harsh conditions.
Resistant to rust and chemical exposure.
8. Custom-Designed Shuttering Magnets
Design: Tailored for specialized formwork needs (e.g., angled, curved, or extra-large forms).
Function: Used in unique construction scenarios where standard magnets don't fit.
Common Uses:
Architectural concrete (complex shapes).
Tunnel lining or precast segment molds.
Advantages:
Solves unconventional formwork challenges.
Can integrate with proprietary form systems.