Precast Concrete System Explained
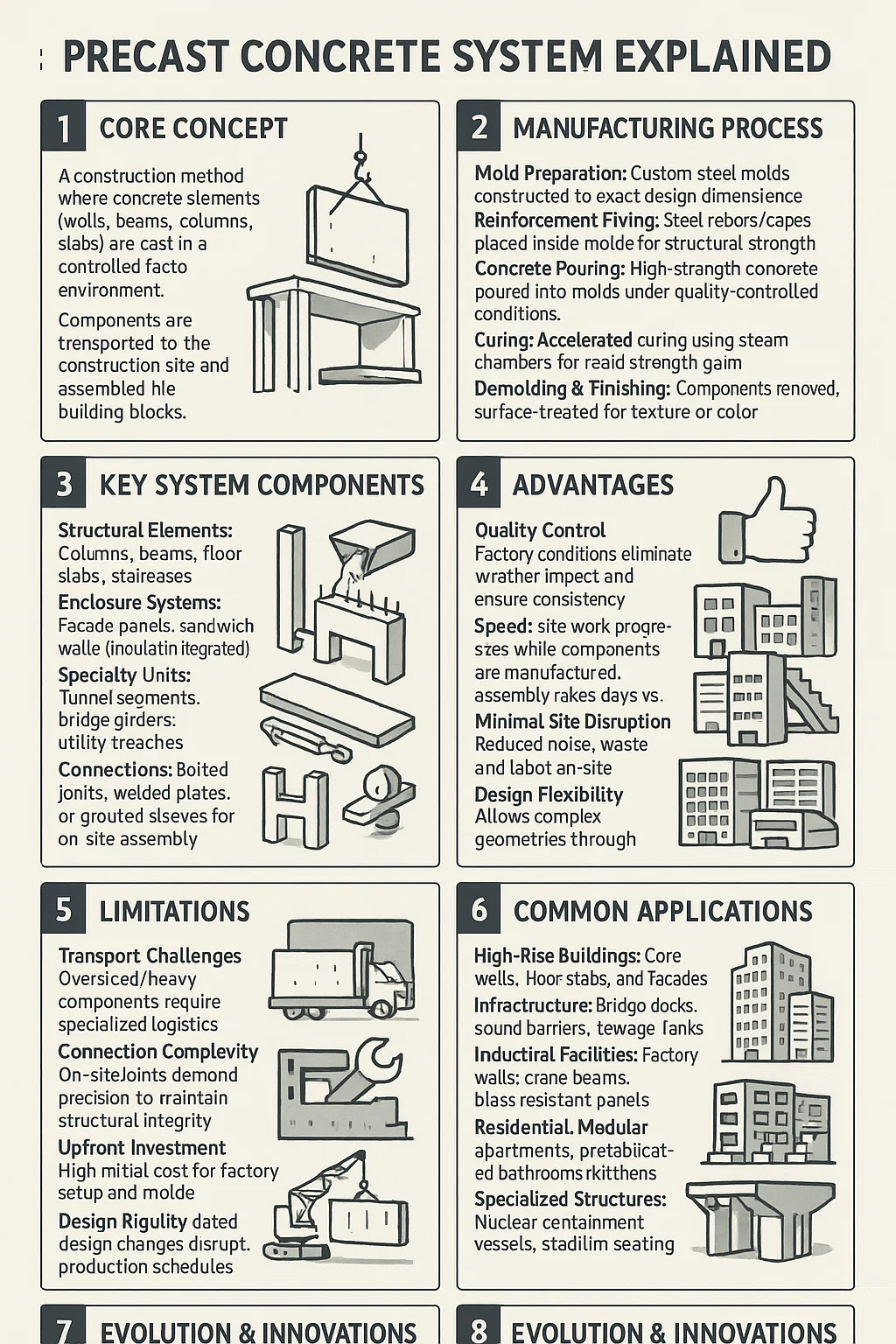
1. Core Concept
A construction method where concrete elements (walls, beams, columns, slabs) are cast in a controlled factory environment.
Components are transported to the construction site and assembled like building blocks.
2. Manufacturing Process
Mold Preparation: Custom steel molds constructed to exact design dimensions.
Reinforcement Fixing: Steel rebars/cages placed inside molds for structural strength.
Concrete Pouring: High-strength concrete poured into molds under quality-controlled conditions.
Curing: Accelerated curing using steam chambers for rapid strength gain.
Demolding & Finishing: Components removed, surface-treated for texture or color.
3. Key System Components
Structural Elements: Columns, beams, floor slabs, staircases.
Enclosure Systems: Façade panels, sandwich walls (insulation integrated).
Specialty Units: Tunnel segments, bridge girders, utility trenches.
Connections: Bolted joints, welded plates, or grouted sleeves for on-site assembly.
4. Advantages
Quality Control: Factory conditions eliminate weather impact and ensure consistency.
Speed: Site work progresses while components are manufactured; assembly takes days vs. weeks.
Minimal Site Disruption: Reduced noise, waste, and labor on-site.
Design Flexibility: Allows complex geometries through custom molds.
Durability: Higher density concrete with optimized curing resists cracks/corrosion.
5. Limitations
Transport Challenges: Oversized/heavy components require specialized logistics.
Connection Complexity: On-site joints demand precision to maintain structural integrity.
Upfront Investment: High initial cost for factory setup and molds.
Design Rigidity: Late design changes disrupt production schedules.
6. Common Applications
High-Rise Buildings: Core walls, floor slabs, and façades.
Infrastructure: Bridge decks, sound barriers, sewage tanks.
Industrial Facilities: Factory walls, crane beams, blast-resistant panels.
Residential: Modular apartments, prefabricated bathrooms/kitchens.
Specialized Structures: Nuclear containment vessels, stadium seating.
7. Site Assembly Workflow
Foundation Prep: Cast foundations with embedded connectors.
Component Delivery: Sequence trucks by assembly order.
Lifting & Placement: Cranes position elements onto bearings/connectors.
Structural Connections: Weld plates, install bolts, or grout sleeves.
Sealing & Finishing: Waterproof joints and apply final finishes.
8. Evolution & Innovations
Hybrid Systems: Combining precast with cast-in-place for complex joints.
Digital Integration: BIM models guide mold design and assembly sequencing.
Sustainability: Recycled aggregates and low-carbon cement in mixes.